Swap all pairwise nodes in a linked list
In this lesson, I will show you an iterative program to swap all pairwise nodes of a linked list.
Are we swapping the pairwise data of nodes or the complete node?
We'll we swapping the nodes, as a result the data will get swapped. Swapping only the element does not make any sense.
For example, if the linked list is 1-2-3-4-5-6 then pairwise swapping all nodes will give us the linked list 2-1-4-3-6-5.
If the linked list is 1-2-3-4-5 then pairwise swapping all nodes will give us the linked list 2-1-4-3-5.
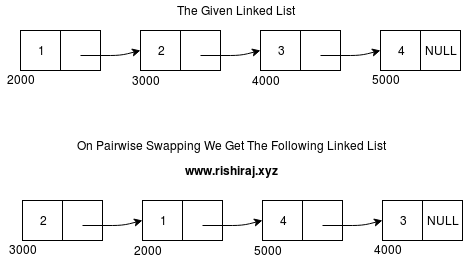
Observe the representation above, the address and data of the nodes.
The following program code require the understanding of insertAfter() function and printList() function.
[code language="C"]
/Pairwise swap all elements of linked list.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void printList(struct Node*);
struct Node* insertAfter(struct Node**, int); //returns adress of last node
void pairWiseSwap(struct Node**);
int main()
{
struct Node *head;
struct Node *endMarker;
head = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
head->data = 1;
head->next = NULL;
endMarker = insertAfter(&head, 2);
endMarker = insertAfter(&endMarker, 3);
endMarker = insertAfter(&endMarker, 4);
endMarker = insertAfter(&endMarker, 5);
endMarker = insertAfter(&endMarker, 6);
pairWiseSwap(&head);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
void pairWiseSwap(struct Node **head){
struct Node *t1, *t2, *beforeT1 = NULL;
int count = 0;
//init
t1 = *head;
t2 = (*head)->next;
while(t1 && t2){
t1->next = t2->next;
t2->next = t1;
if(count == 0)
(*head) = t2;
else{
beforeT1->next = t2;
}
beforeT1 = t2;
if(t2->next == NULL)
t1 = NULL;
else
t1 = t1->next; //t1 = t1->next;
if(t1 == NULL)
t2 = NULL;
else
t2 = t1->next;
count++;
beforeT1 = beforeT1->next;
}
}
void printList(struct Node* node){
int count=0;
while(node!=NULL){
printf("\t%d", node->data);
node = node->next;
count++;
}
printf("\nTotal nodes printed=\t%d\n", count);
}
struct Node* insertAfter(struct Node **node, int data){
if( (*node)==NULL) {
printf("Node Does Not Exists\n");
return NULL;
}
struct Node *new = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new->data = data;
new->next = (*node)->next;
(*node)->next = new;
return new;
}
[/code]